EXPERT WOUND CARE FOR LASTING RECOVERY
We Treat Chronic, Slow-Healing, and Post-Surgical Wounds Using Innovative Medical Solutions
Effective wound care focuses on cleaning, promoting healing, and preventing infection. This includes removing debris, irrigating the wound with sterile saline, applying a thin layer of antibiotic ointment (like bacitracin or petroleum jelly), and covering it with a sterile dressing. It also involves monitoring for signs of infection and seeking professional care for deep or complex wounds.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Cleaning:
-
Initial Cleaning:
Immediately after the injury, thoroughly wash the wound with clean water and mild soap to remove visible dirt and debris. -
Wound Irrigation:
Use sterile saline to flush out any remaining debris. Avoid using harsh cleansers like hydrogen peroxide or alcohol, as they can damage healthy tissue. - Regular Cleaning: Clean the wound twice daily with soap and water, and apply a fresh bandage and ointment.
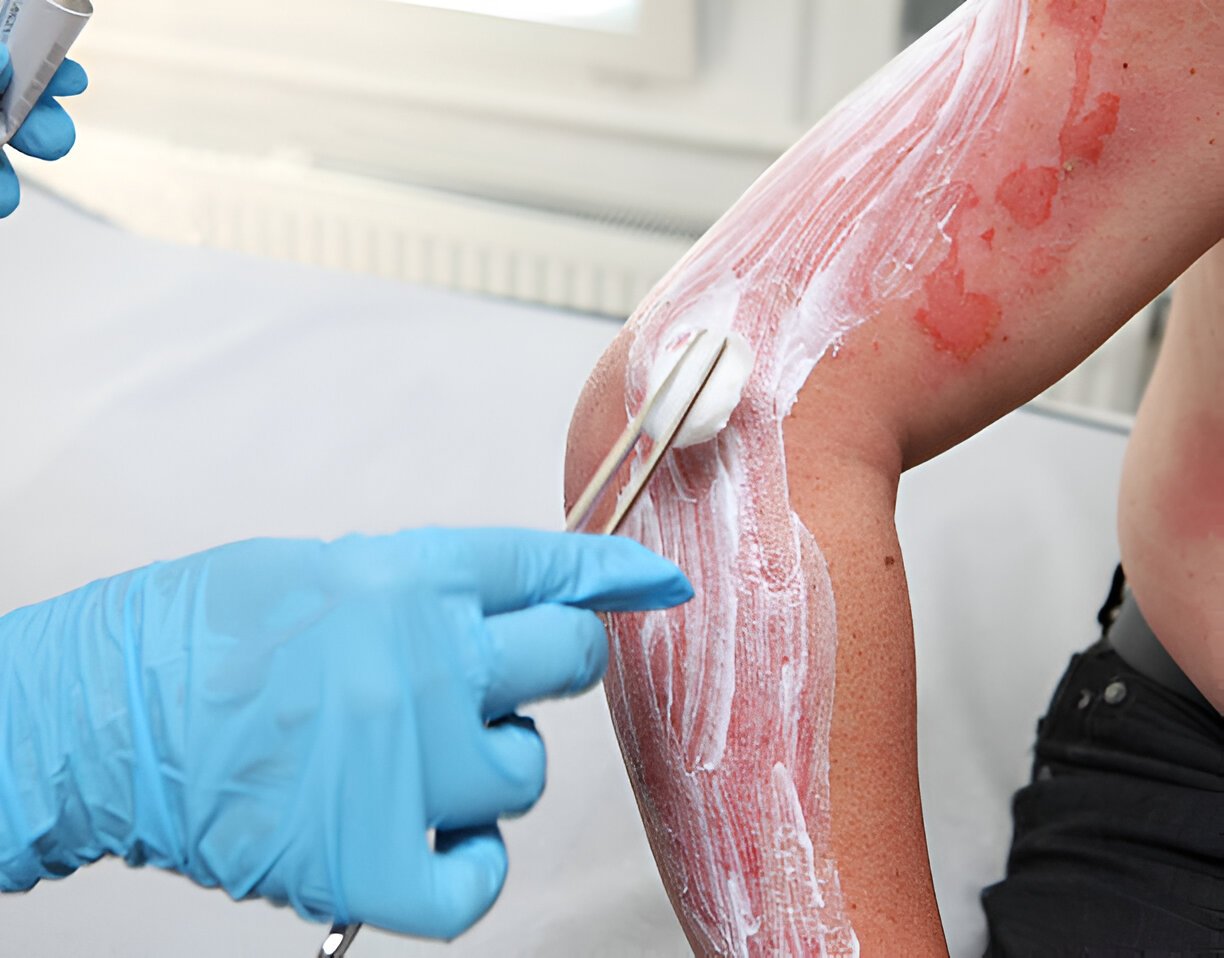
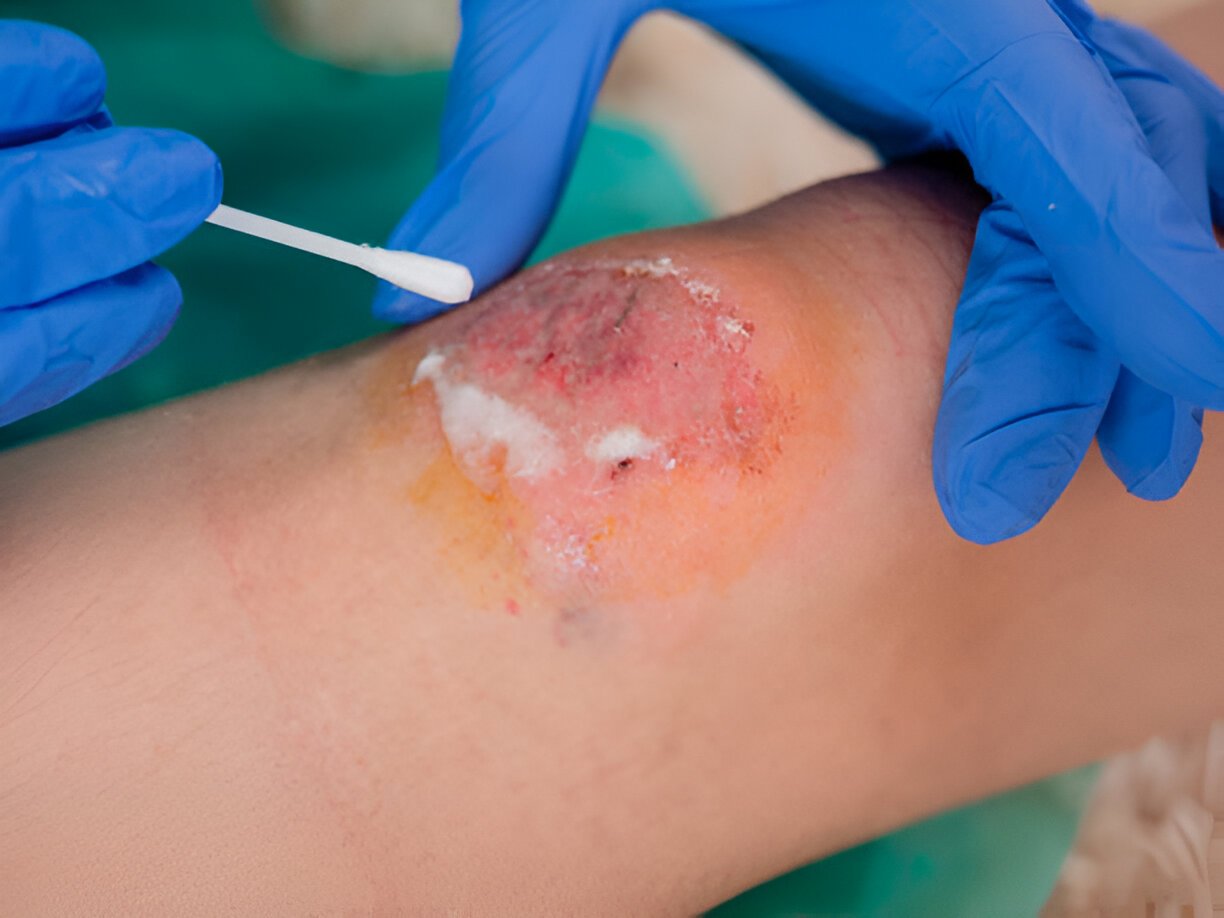
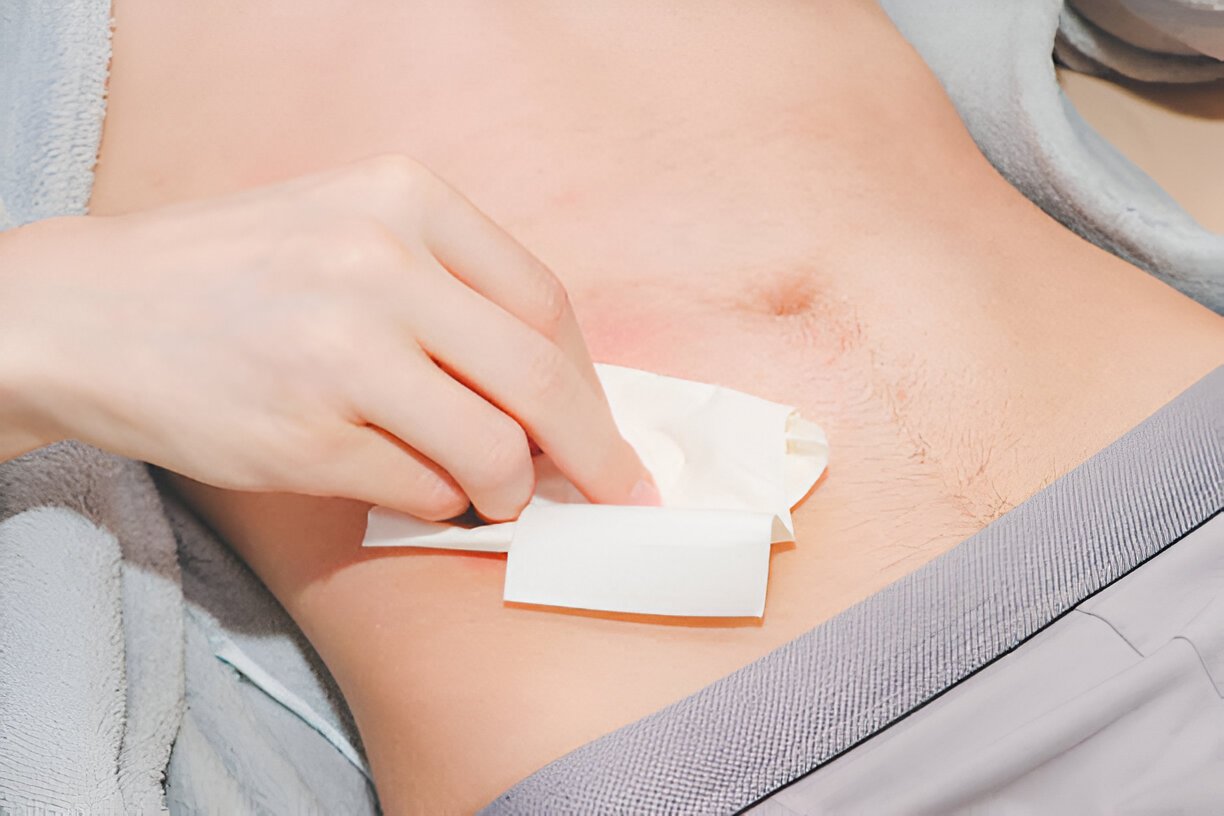
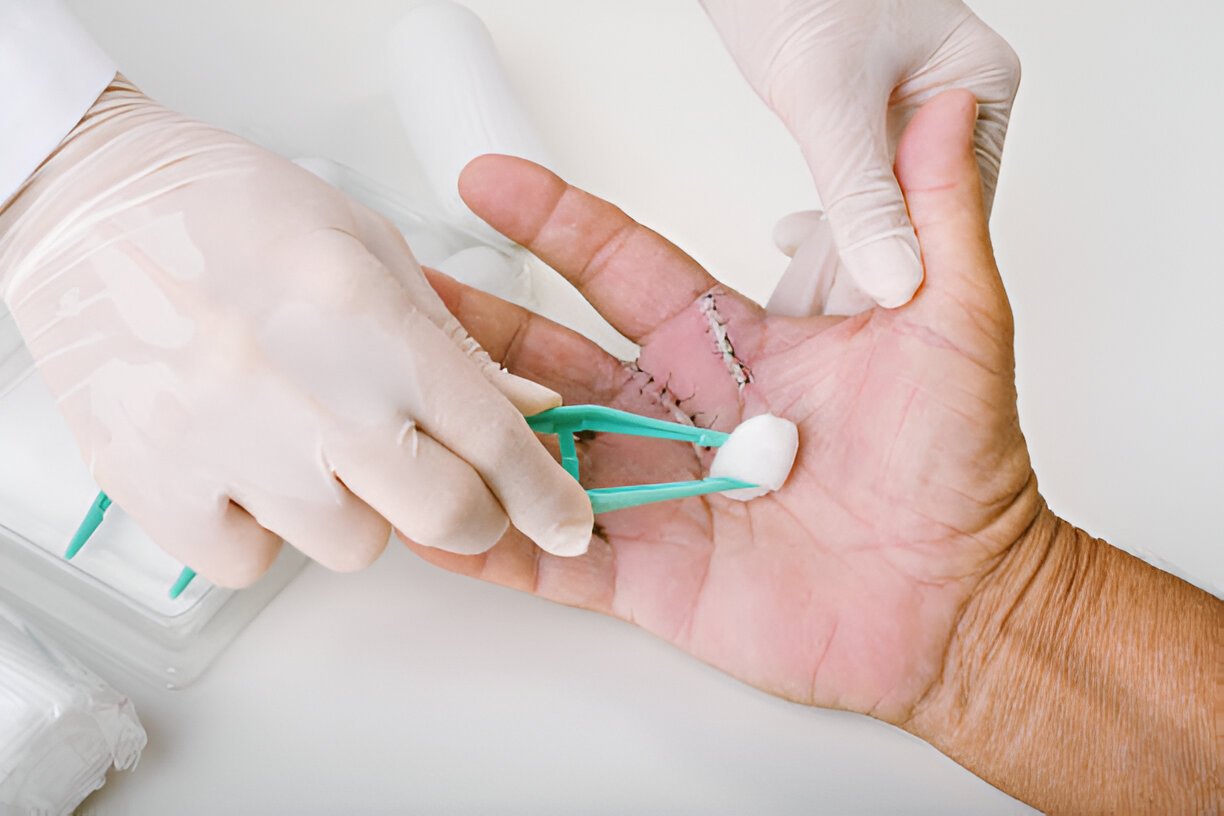
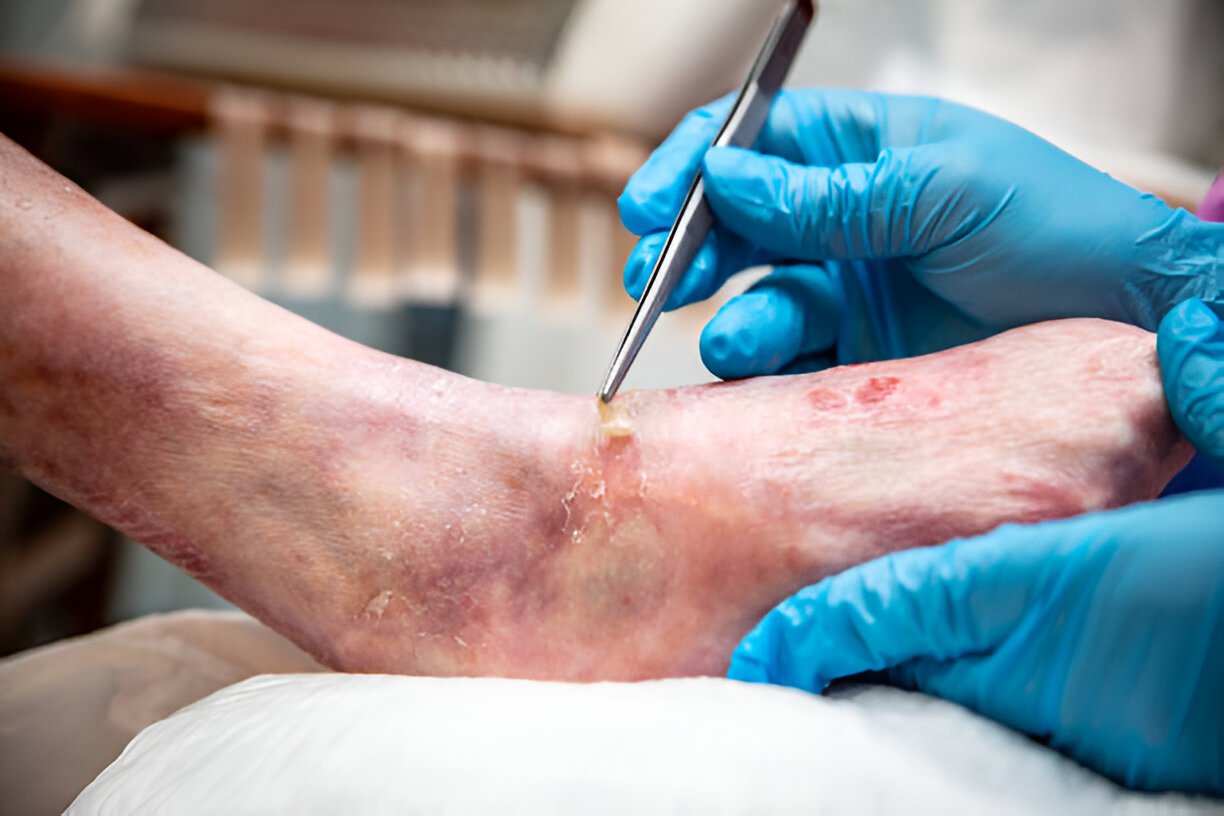
Facilitating Faster Healing and Preventing Complications:
-
Promotes Efficient Healing:
Effective wound care creates an optimal environment for the body's natural healing mechanisms, helping tissues regenerate and wounds close more quickly. -
Reduces Risk of Infection:
By implementing proper cleaning and dressing techniques, wound care helps prevent infections, which can lead to serious complications and even sepsis. -
Minimizes Scarring:
Good wound care practices can support natural healing and reduce the likelihood of significant scarring, which can impact both function and appearance.
Improving Physical Comfort and Function:
-
Pain Management:
Wound care specialists employ various strategies to manage wound-related pain, including appropriate dressings, pain medications, and non-pharmacological interventions. This enhances patient comfort and adherence to treatment. -
Enhanced Mobility and Functionality:
For individuals with chronic wounds, especially those affecting lower extremities, wound care can help improve mobility and functionality, leading to a better quality of life.





Addressing Psychological and Emotional Well-being:
-
Comprehensive Psychological Support:
Wound care professionals address the emotional and psychological impact of wounds, recognizing that chronic wounds can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. -
Emotional Support and Education:
Wound care includes providing emotional support, patient education, and counseling services. Educating patients about the healing process and setting realistic expectations can reduce anxiety and uncertainty. -
Empowering Patients:
By involving patients in their care plans and teaching them self-management techniques, wound care fosters a sense of ownership and control, which can improve adherence to treatment and outcomes.
Enhancing Overall Quality of Life:
-
Holistic Approach:
Patient-centered wound care considers the physical, emotional, psychological, and social dimensions of patient well-being, leading to better outcomes and enhanced quality of life. -
Reduced Healthcare Costs:
Effective wound care can promote faster healing and prevent complications, potentially leading to shorter hospital stays and reduced healthcare costs.

In essence, wound care contributes to optimal health and well-being by not only addressing the physical injury but also by supporting the individual's emotional and psychological needs throughout the healing journey.
Enhancing Overall Quality of Life:
-
Holistic Approach:
Patient-centered wound care considers the physical, emotional, psychological, and social dimensions of patient well-being, leading to better outcomes and enhanced quality of life. -
Reduced Healthcare Costs:
Effective wound care can promote faster healing and prevent complications, potentially leading to shorter hospital stays and reduced healthcare costs.


Detail Treatment Options and Therapies:
-
List common wound types treated:
Include examples such as burns, diabetic foot ulcers, surgical wounds, and hard-to-heal wounds. -
treatments:
Mention therapies like hyperbaric oxygen therapy, debridement, negative pressure wound therapy, wound dressings, and skin grafting.